
Our Products

Sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate, also known as baking soda, has a variety of medicinal uses. Sodium bicarbonate is sometimes used as an antacid to treat heartburn and indigestion. It can also be used to treat conditions such as acidosis (a condition in which the blood is too acidic) or to help reduce the effects of certain poisons or medications.It's worth noting that while sodium bicarbonate is generally safe for many uses, it can cause irritation or harm if used improperly or in excessive amounts. It's important to always follow instructions and use caution when handling sodium bicarbonate.
Sodium bicarbonate is commonly used in nephrology, which is the study and treatment of kidney diseases. Some of the uses of sodium bicarbonate in nephrology includes:
Acidosis treatment: Sodium bicarbonate is used to treat metabolic acidosis, a condition where the body produces too much acid or cannot remove enough acid.
This can be caused by kidney disease, diabetes, or other health conditions. Sodium bicarbonate works by neutralizing the acid in the blood and restoring the body's normal pH balance.
Dialysis: Sodium bicarbonate is often used during hemodialysis, a treatment for kidney failure. Haemodialysis removes waste and excess fluid from the blood, but can also cause metabolic acidosis. Sodium bicarbonate is used to correct this acidosis and maintain a healthy pH balance.
Contrast-induced nephropathy prevention: Sodium bicarbonate has been studied for its potential to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy, a type of kidney damage that can occur after imaging tests involving contrast dye. Some studies suggest that using sodium bicarbonate instead of saline (salt water) as a hydration solution during these tests may reduce the risk of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Prevention of kidney stones: Some studies have suggested that sodium bicarbonate supplementation may help to prevent the formation of kidney stones. This is because sodium bicarbonate can increase the pH of urine, which can help to prevent the formation of crystals that can lead to kidney stones.
Urine alkalinization: In some cases, sodium bicarbonate may be used to alkalinize the urine, which can help to prevent certain types of kidney stones and urinary tract infections.
It's important to note that the use of sodium bicarbonate in nephrology should always be under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional. Dosage and treatment protocols may vary depending on the patient's condition and medical history.

Alpha Keto Analogues
Keto analogues, also known as ketoanalogues, are a group of supplements used in nephrology to help manage patients with chronic kidney disease. (CKD) by providing a source of essential amino acids that are restricted in the patient's diet.Keto analogues are made up of a mixture of amino acids that are chemically similar to the essential amino acids that are commonly restricted in the diets of patients with CKD.
These supplements are intended to help prevent the buildup of uremic toxins that can lead to complications in patients with CKD.
The primary use of keto analogues in nephrology is to help slow the progression of CKD and delay the need for dialysis. They are usually prescribed to patients with stage 3 or 4 CKD who have low protein diets and high levels of urea in their blood.
It's important to note that keto analogues are not a substitute for a low protein diet and should always be used under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional.

N-acetylcysteine NAC and Taurine
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and Taurine are both used in nephrology for their potential therapeutic effects on kidney function. NAC is an antioxidant and a precursor to glutathione, a natural substance in the body that helps protect cells from oxidative damage.NAC has been studied as a treatment for various kidney-related conditions, including contrast-induced nephropathy, a type of acute kidney injury that can occur after imaging procedures involving contrast agents. NAC may help protect the kidneys from the toxic effects of these agents.
Taurine is an amino acid that is found in high concentrations in the kidneys, among other organs. It has been studied for its potential effects on kidney function in various contexts, including chronic kidney disease and diabetic nephropathy.
Taurine may help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the kidneys, as well as improve kidney function by promoting the excretion of waste products.
Both NAC and Taurine are generally considered safe for use in humans, although they may have some side effects in certain individuals. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using either of these substances for any kidney-related condition.

Febuxostat
Febuxostat is a medication used to lower high levels of uric acid in the blood. It is primarily used to treat gout, a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, which can cause intense pain, swelling, and redness.By lowering uric acid levels, Febuxostat can help prevent gout attacks and reduce the risk of gout-related complications such as joint damage and kidney stones.
Febuxostat works by inhibiting xanthine oxidase, an enzyme that is involved in the production of uric acid in the body. By reducing the activity of this enzyme, febuxostat decreases the amount of uric acid that is produced and helps to lower the level of uric acid in the blood.
Febuxostat is available in tablet form and is typically taken once a day, with or without food. The dose and duration of treatment may vary depending on the individual's condition and response to the medication, and should be determined by a healthcare provider.

Clonidine
Clonidine is a medication that is primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It is classified as an alpha-2 agonist, which means it works by stimulating alpha-2 receptors in the brain, leading to a decrease in sympathetic nervous system activity, which helps lower blood pressure.In addition to its use for hypertension, clonidine has also been found to be effective for a range of other conditions, including:
1. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Clonidine is sometimes prescribed off-label to treat ADHD, particularly in children who do not respond well to other medications.
2. Opioid withdrawal: Clonidine can help alleviate symptoms of opioid withdrawal, including anxiety, agitation, sweating, and restlessness.
3. Anxiety disorders: Clonidine can be used off-label to treat anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
4. Tourette's syndrome: Clonidine can help alleviate tics and other symptoms of Tourette's syndrome.
5. Menopausal symptoms: Clonidine can be used off-label to treat hot flashes and other symptoms of menopause.
It is important to note that while clonidine can be effective for these conditions, it should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional. Clonidine can have side effects, and it can interact with other medications. Your doctor can help you determine whether clonidine is an appropriate treatment option for your specific needs.

Cilnidipine
Cilnidipine is a calcium channel blocker used for the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure). It works by blocking the entry of calcium into the smooth muscle cells of the blood vessels, which results in the relaxation of blood vessels and a decrease in blood pressure.
Cilnidipine is unique compared to other calcium channel blockers because it blocks both L-type and N-type calcium channels. This dual action of Cilnidipine may provide additional benefits over other calcium channel blockers in the treatment of hypertension, such as improved renal blood flow, decreased proteinuria, and improved endothelial function.
Cilnidipine is typically taken orally, with or without food, and the dosage may vary depending on the patient's individual needs and response to the medication.
Like all medications, cilnidipine may have potential side effects, including dizziness, headache, flushing, and peripheral edema. It is important to talk to a healthcare professional before starting or stopping any medication.

Ferrous Ascorbate with vitamins
In Iron deficiency anemia FIZB is a comprehensive combination for iron deficiency anemia and for various metabolic and enzymatic activities.FIZB is a combination of B1 , B2 , B3, B5, B6, B 7 ,B9 , B12 along with elemental Iron ferrous ascorbate.
FiZB contains all water soluble Vitamin which helps as coenzyme in more than 100 enzymatic processes.
Ferrous Ascorbate: Ferrous Ascorbate is a combination of iron and vitamin C. It is used for iron deficiency and anemia. Iron replenishes the body's iron stores, correcting iron deficiency anemia.
Vitamin C (ascorbate) promotes the absorption of iron in the body.
Mechanism of Action: Ferrous Ascorbate facilitates the transport and utilization of oxygen. It helps in cell growth and proliferation, improving the production of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
Folic Acid (Vitamin B9): Folic acid is essential for the production of red blood cells. It prevents and treats folate deficiency and anemia. During pregnancy, folic acid plays a vital role in the development of the unborn baby's brain and spinal cord. DNA and Genetic Material: Folic acid helps make DNA and genetic material.
Red Blood Cell Formation: It is essential for the production of red blood cells. Preventing Birth Defects: Sufficient folic acid intake before and during pregnancy reduces the risk of certain birth defects. Nervous System Health: B9 supports the nervous system, liver, skin, hair, and eyes.
Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin): Vitamin B12 is crucial for red blood cell formation. It helps maintain healthy nerve cells and supports DNA synthesis. Deficiency can lead to pernicious anemia and neurological symptoms.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Vitamin B6 is involved in hemoglobin synthesis. It supports the production of neurotransmitters and helps maintain a healthy immune system. Deficiency may contribute to anemia and other health issues.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid): B5 is involved in energy metabolism and the synthesis of coenzyme A. It supports healthy skin, hair, and eyes. Sources: Found in various foods, including meat, eggs, whole grains and vegetables.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine): Thiamine is essential for carbohydrate metabolism and energy production. It supports nerve function and overall well-being. Sources: Whole grains, legumes, nuts, and pork are good sources of B1.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): B2 is crucial for energy production, growth, and red blood cell formation. It also plays a role in maintaining healthy skin and vision.
Sources: Dairy products, eggs, green leafy vegetables and lean meats provide riboflavin.
Biotin Deficiency: Biotin (also known as vitamin B7 is essential for the body. It plays a crucial role in energy metabolism, specifically in the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and amino acids. Biotin deficiency can lead to symptoms such as thinning hair and a red, scaly rash around the eyes, nose, and mouth.
Treatment: Taking biotin by mouth or through a shot can treat and prevent low blood levels of biotin. Doses of up to 10 mg daily have been used for this purpose.
Hair Loss and Brittle Nails: Biotin is commonly used for hair loss and brittle nails. However, scientific evidence supporting these uses is limited.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): High-dose biotin by mouth does not reduce disability in people with MS. It also doesn't seem to affect the risk of relapse.
Rough, Scaly Skin (Seborrheic Dermatitis): Taking biotin does not significantly improve rash in infants with seborrheic dermatitis.
Interactions and Precautions: Biotin supplements might interfere with some lab tests. Consult your doctor if you are taking biotin supplements and need blood tests.
Biotin is generally safe when taken by mouth or applied to the skin. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is likely safe when used in recommended amounts. In summary, these nutrients play vital roles in maintaining healthy blood cells, preventing anemia, and supporting overall well-being.

Dapagliflozin
Dapagliflozin is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs known as SGLT2 inhibitors, which work by reducing the amount of glucose that is reabsorbed by the kidneys and increasing the amount of glucose that is excreted in urine.When taken as directed by a healthcare provider, Dapagliflozin can help lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. It is usually taken once daily by mouth and may be prescribed alone or in combination with other diabetes medications.
In addition to its blood sugar-lowering effects, Dapagliflozin has also been shown to have benefits for people with heart failure and/or a history of cardiovascular disease.
It can help reduce the risk of hospitalization for heart failure and improve survival in certain patients.
As with any medication, Dapagliflozin can have side effects, and it may not be appropriate for everyone.
It's important to talk to a healthcare provider about the risks and benefits of this medication and any other medications you may be taking before starting treatment.
Nephrology (IgA Nephropathy):
IgA nephropathy is a chronic immune-mediated kidney disease and a major cause of kidney failure worldwide. The gut mucosal immune system is implicated in its pathogenesis.IGBUDA a novel oral targeted-release formulation of budesonide, is designed to act at the gut mucosal level. IGBUDA is an oral, enteric coated control release formulation of the corticosteroid budesonide.
It remains intact until it reaches the ileum, where it targets mucosal B cells, including those in the Peyer's patches. These patches are responsible for the production of galactose-deficient IgA1, believed to underlie IgA nephropathy.
In summary, targeted-release budesonide IGBUDA holds promise in treating IgA nephropathy by acting at the gut mucosal level and modifying key pathogenic biomarkers. Additionally, it is used as an add-on to standard care in nephrology, demonstrating better efficacy than standard care alone.
IgA Nephropathy a kidney disorder characterized by the accumulation of a protein called immunoglobulin A (IgA) in the kidneys.
Cause and Mechanism: IgA nephropathy occurs when abnormal IgA antibodies build up in the kidneys. These antibodies get trapped in the kidney tissues, leading to inflammation and damage. Over time, this process can impair kidney function and potentially progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), which is kidney failure.
Symptoms: In the early stages, IgA nephropathy often doesn't cause noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
Hematuria: Blood in the urine, which can give the urine a cola- or tea-colored appearance. Proteinuria: Leakage of protein into the urine, resulting in foamy urine.
Back Pain: Pain on one or both sides of the back below the ribs.
Edema: Swelling in the hands and feet. High Blood Pressure, Weakness and Fatigue, Progressive IgA nephropathy tends to worsen gradually over years. This is a progressive disease
Streptococcus Thermophilus 15/30 Billion Spores
Lactobacillus Acidophilus 15/30 Billion Spores
Bifidobacterium Longum 15/30 Billion Spores
Fructo-Oligosaccharides 100 mg
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a global health concern, often associated with metabolic conditions like obesity and type 2 diabetes. Patients with CKD face additional comorbidities such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular issues, gastrointestinal problems, and cognitive decline.
Traditional therapies include managing comorbidities or using replacement treatments like peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis or organ transplantation.
One intriguing area of study is uremic toxins (UT), which accumulate excessively during CKD due to food metabolism or renal function loss. High urea concentrations significantly alter the gut microbiota, leading to a decrease in anti-inflammatory bacterial strains and an increase in strains that metabolize urea but also produce UTs like indoxyl sulfate and p-cresol sulfate. These UTs activate cellular processes causing oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis, primarily affecting the gut, heart and kidneys.
Prebiotics promote the growth of specific beneficial bacteria species, reduce inflammation, improve metabolic function, and decrease serum concentrations of p-cresol and indoxyl sulfate. Additionally, they decrease cecal indoles and enhance renal function, stress markers, and apoptosis1.
Probiotics, on the other hand, have demonstrated their ability to remove uremic toxins and may slow down renal disease progression. While their precise role in managing renal failure is still being defined, early data suggest that probiotics could play a significant part in chronic kidney disease management2.
However, further research is needed to explore the use of prebiotics and probiotics in larger sample sizes. Identifying useful bacterial strains, optimal dosages, and treatment durations will be crucial to affirm their potential as beneficial complements to CKD treatment.
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits to the host. These friendly bacteria play a crucial role in maintaining gut health and overall well-being.
Probiotics and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Dysbiosis, an imbalance in gut microbiota, is common in CKD patients. Probiotics aim to restore this balance by increasing beneficial bacteria. While high-quality interventional studies are still limited, some findings suggest potential benefits:
Reduction in Uremic Toxins and Inflammation: A meta-analysis found that probiotics may reduce levels of PCS (p-cresyl sulfate) and the pro-inflammatory cytokine Interleukin-6 (IL-6) in CKD patients.
Decrease in Serum CRP (C-reactive Protein) and Gastrointestinal Symptoms: A small clinical trial observed positive effects on CRP and gastrointestinal symptoms in hemodialysis patients using a symbiotic gel containing Omega-3s, vitamins, inulin, and specific probiotic strains1.
Prebiotics for Gut Health: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that nourish beneficial gut bacteria. Some kidney-friendly sources of prebiotics include: Garlic, Onions, Leeks, Apples , Flaxseeds, Asparagus , Unripe bananas , Barley , Oats, Cocoa, Wheat bran, Chicory root , Seaweed.
While probiotics can be beneficial, they are most effective when combined with a healthy balanced diet rich in fiber and prebiotics.
Remember, taking a pill or powder cannot replace the effects of a poor diet. Prioritize overall nutrition for better kidney and gut health in CKD patients1
Lactobacillus Acidophilus 15/30 Billion Spores
Bifidobacterium Longum 15/30 Billion Spores
Fructo-Oligosaccharides 100 mg
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a global health concern, often associated with metabolic conditions like obesity and type 2 diabetes. Patients with CKD face additional comorbidities such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular issues, gastrointestinal problems, and cognitive decline.
Traditional therapies include managing comorbidities or using replacement treatments like peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis or organ transplantation.
One intriguing area of study is uremic toxins (UT), which accumulate excessively during CKD due to food metabolism or renal function loss. High urea concentrations significantly alter the gut microbiota, leading to a decrease in anti-inflammatory bacterial strains and an increase in strains that metabolize urea but also produce UTs like indoxyl sulfate and p-cresol sulfate. These UTs activate cellular processes causing oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis, primarily affecting the gut, heart and kidneys.
Prebiotics promote the growth of specific beneficial bacteria species, reduce inflammation, improve metabolic function, and decrease serum concentrations of p-cresol and indoxyl sulfate. Additionally, they decrease cecal indoles and enhance renal function, stress markers, and apoptosis1.
Probiotics, on the other hand, have demonstrated their ability to remove uremic toxins and may slow down renal disease progression. While their precise role in managing renal failure is still being defined, early data suggest that probiotics could play a significant part in chronic kidney disease management2.
However, further research is needed to explore the use of prebiotics and probiotics in larger sample sizes. Identifying useful bacterial strains, optimal dosages, and treatment durations will be crucial to affirm their potential as beneficial complements to CKD treatment.
BIOBAR in nephrology:
What Are Probiotics ?Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits to the host. These friendly bacteria play a crucial role in maintaining gut health and overall well-being.
Probiotics and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Dysbiosis, an imbalance in gut microbiota, is common in CKD patients. Probiotics aim to restore this balance by increasing beneficial bacteria. While high-quality interventional studies are still limited, some findings suggest potential benefits:
Reduction in Uremic Toxins and Inflammation: A meta-analysis found that probiotics may reduce levels of PCS (p-cresyl sulfate) and the pro-inflammatory cytokine Interleukin-6 (IL-6) in CKD patients.
Decrease in Serum CRP (C-reactive Protein) and Gastrointestinal Symptoms: A small clinical trial observed positive effects on CRP and gastrointestinal symptoms in hemodialysis patients using a symbiotic gel containing Omega-3s, vitamins, inulin, and specific probiotic strains1.
Prebiotics for Gut Health: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that nourish beneficial gut bacteria. Some kidney-friendly sources of prebiotics include: Garlic, Onions, Leeks, Apples , Flaxseeds, Asparagus , Unripe bananas , Barley , Oats, Cocoa, Wheat bran, Chicory root , Seaweed.
While probiotics can be beneficial, they are most effective when combined with a healthy balanced diet rich in fiber and prebiotics.
Remember, taking a pill or powder cannot replace the effects of a poor diet. Prioritize overall nutrition for better kidney and gut health in CKD patients1

Coenzyme Q10 with Omega - 3 - Fatty acids and other antioxidants
Role of Coq10 in Nephrology
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) has been studied for its potential roles and benefits in various kidney-related conditions:
Antioxidant Properties: CoQ10 is a powerful antioxidant that helps neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. This oxidative stress is known to contribute to kidney damage in conditions like chronic kidney disease (CKD) and diabetic nephropathy. CoQ10's antioxidant properties may help protect kidney cells from damage and slow down the progression of these conditions.
Energy Production: CoQ10 is a crucial component of the electron transport chain in mitochondria, where it helps generate ATP, the cell's primary energy source. Kidneys are highly energy-demanding organs, and maintaining proper energy production is essential for their function. CoQ10 supplementation may support energy production in kidney cells and help maintain their health.
Endothelial Function and Blood Pressure Regulation: CoQ10 has been explored for its potential role in improving endothelial function, which is important for blood vessel health. In conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure), impaired endothelial function is a contributing factor. CoQ10's ability to improve endothelial function might have positive effects on blood pressure regulation and overall cardiovascular health, which is closely tied to kidney health.
Inflammation Reduction: Inflammation plays a significant role in the progression of kidney diseases. CoQ10's anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce inflammation in the kidneys, potentially slowing down the damage caused by chronic inflammation in conditions like CKD.
Mitochondrial Support: Kidney cells have a high energy requirement due to their role in filtration and maintaining electrolyte balance. CoQ10's involvement in mitochondrial function and energy production can potentially support the health and efficiency of kidney cells.
Potential Support for Dialysis Patients: Patients undergoing dialysis often experience CoQ10 depletion due to oxidative stress and the dialysis process itself. CoQ10 supplementation might help counteract this depletion and improve overall well-being in dialysis patients.
Kidney Health: Omega 3 may benefit kidney function by reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health, which is crucial for kidney health.
Kidney Health: L-Carnitine supplementation has been studied in kidney disease patients. It may help improve anemia, muscle weakness, and overall well-being.
Kidney Health: L-Arginine may help improve blood flow to the kidneys and support their function.
Kidney Health: Lycopene may help protect kidney cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. If you have any specific health concerns, it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
Role of Coq10 in Nephrology
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) has been studied for its potential roles and benefits in various kidney-related conditions:
Antioxidant Properties: CoQ10 is a powerful antioxidant that helps neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. This oxidative stress is known to contribute to kidney damage in conditions like chronic kidney disease (CKD) and diabetic nephropathy. CoQ10's antioxidant properties may help protect kidney cells from damage and slow down the progression of these conditions.
Energy Production: CoQ10 is a crucial component of the electron transport chain in mitochondria, where it helps generate ATP, the cell's primary energy source. Kidneys are highly energy-demanding organs, and maintaining proper energy production is essential for their function. CoQ10 supplementation may support energy production in kidney cells and help maintain their health.
Endothelial Function and Blood Pressure Regulation: CoQ10 has been explored for its potential role in improving endothelial function, which is important for blood vessel health. In conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure), impaired endothelial function is a contributing factor. CoQ10's ability to improve endothelial function might have positive effects on blood pressure regulation and overall cardiovascular health, which is closely tied to kidney health.
Inflammation Reduction: Inflammation plays a significant role in the progression of kidney diseases. CoQ10's anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce inflammation in the kidneys, potentially slowing down the damage caused by chronic inflammation in conditions like CKD.
Mitochondrial Support: Kidney cells have a high energy requirement due to their role in filtration and maintaining electrolyte balance. CoQ10's involvement in mitochondrial function and energy production can potentially support the health and efficiency of kidney cells.
Potential Support for Dialysis Patients: Patients undergoing dialysis often experience CoQ10 depletion due to oxidative stress and the dialysis process itself. CoQ10 supplementation might help counteract this depletion and improve overall well-being in dialysis patients.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Function: Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for overall health. They have anti-inflammatory properties, support heart health and may help reduce triglyceride levels.Kidney Health: Omega 3 may benefit kidney function by reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health, which is crucial for kidney health.
L-Carnitine:
Function: L-Carnitine is involved in energy metabolism and fatty acid transport.Kidney Health: L-Carnitine supplementation has been studied in kidney disease patients. It may help improve anemia, muscle weakness, and overall well-being.
L-Arginine:
Function: L-Arginine is an amino acid that supports blood vessel health and circulation.Kidney Health: L-Arginine may help improve blood flow to the kidneys and support their function.
Lycopene:
Function: Lycopene is a potent antioxidant found in tomatoes and other red fruits.Kidney Health: Lycopene may help protect kidney cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. If you have any specific health concerns, it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
EMPAM 10/25 MG (Empagliflazon) this is a medication used in type 2 DM , CKD , HF
This belongs to SGLT 2 inhibitors which prevents Glucose reabsorption in the Kidney reduce hyperglycemia, HT and have a organ protection benifits. EMPAM have a dual action makes a groundbreaking therapy for managing type 2 DM , chronic kidney disease, and heart failure.
EMPAM cardiovascular benefits extend beyond glucose control: EMPAM reduces preload, afterload and improve heart function. EMPAM enhances tubuloglomerular feedback, which decreases intraglomerular pressure and systemic blood pressure and preserve Kidney function
EMPAM had shown to reduce primary composite out come of hospitalizations , Mortality and Morbidity in heart failure patient.
Empam is administered orally, once daily in the morning, with or without food. The dosage varies based on the patient's condition and renal function.
Dosage for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
Initial dose: 10 mg once daily, which can be increased to 25 mg once daily for additional glycemic control.
Maximum dose: 25 mg daily
Dosage for Heart Failure or Chronic Kidney Disease: Usual dose: 10mg once daily
Administration Tips:
- Swallow the tablets whole with water.
- Do not chew or crush the tablets.
- Take the medication at the same time every day, with or without food ³.
EMPAM feature and benifit
1. Inhibition of Sodium-Hydrogen Exchanger (NHE) - Empagliflozin reduces intracellular pH and calcium signaling by inhibiting NHE. This decreases fibroblast activity and collagen production, which are key contributors to fibrosis[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://cardiab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12933-023-01756-0?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "1").
2. Reduction of Oxidative Stress - It lowers oxidative stress by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which helps prevent tissue damage and fibrosis[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/18/3/313?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "2").
3. Modulation of Fibrotic Pathways - Empagliflozin inhibits the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway, a major driver of fibrosis, thereby reducing extracellular matrix deposition[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://cardiab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12933-021-01322-6?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "3
Recent Clinical Trials on Empagliflozin
1. **EMPACT-MI Phase III Trial**: This trial investigated the effect of empagliflozin (Jardiance) on the risk of heart failure hospitalization and death in adults following a heart attack. The trial showed a 10% relative risk reduction in the primary composite endpoint of time to first hospitalization due to heart failure or all-cause mortality for empagliflozin versus placebo(https://www.boehringer-ingelheim.com/human-health/heart-diseases/results-jardiance-empact-mi-phase-iii-trial?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "1").
2. **Comparative Outcomes of Empagliflozin to Dapagliflozin in Patients With Heart Failure**: This cohort study compared the outcomes of empagliflozin and dapagliflozin in reducing all-cause mortality and hospitalizations in patients with heart failure. The study found that patients who started using empagliflozin were less likely to experience the primary outcome of composite of all-cause mortality or hospitalization compared with those who started using dapagliflozin[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2818219?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "2").
3. **EMPEROR-Reduced Trial**: This trial assessed the safety and efficacy of empagliflozin in patients with symptomatic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), irrespective of diabetes status. The trial showed that empagliflozin is superior to placebo in improving heart failure outcomes among patients with HFrEF[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/clinical-trials/2020/08/28/16/12/emperor-reduced?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "3").
If you have any specific questions or need more detailed information or full text article feel free to ask or send a mail arunthakur@p4medicine.in
Above is a medical information only not for use please consult your doctor for any query.
This belongs to SGLT 2 inhibitors which prevents Glucose reabsorption in the Kidney reduce hyperglycemia, HT and have a organ protection benifits. EMPAM have a dual action makes a groundbreaking therapy for managing type 2 DM , chronic kidney disease, and heart failure.
EMPAM cardiovascular benefits extend beyond glucose control: EMPAM reduces preload, afterload and improve heart function. EMPAM enhances tubuloglomerular feedback, which decreases intraglomerular pressure and systemic blood pressure and preserve Kidney function
EMPAM had shown to reduce primary composite out come of hospitalizations , Mortality and Morbidity in heart failure patient.
Empam is administered orally, once daily in the morning, with or without food. The dosage varies based on the patient's condition and renal function.
Dosage for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
Initial dose: 10 mg once daily, which can be increased to 25 mg once daily for additional glycemic control.
Maximum dose: 25 mg daily
Dosage for Heart Failure or Chronic Kidney Disease: Usual dose: 10mg once daily
Special Considerations:
Renal Impairment: Not recommended for patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m²) or end-stage renal disease. Discontinue if eGFR falls below 45 mL/min/1.73 m². Hepatic Impairment :- No dosage adjustment is required for mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment. Elderly :- Not recommended for patients aged 85 years or older ⁴ ⁵.Administration Tips:
- Swallow the tablets whole with water.
- Do not chew or crush the tablets.
- Take the medication at the same time every day, with or without food ³.
EMPAM feature and benifit
1. Inhibition of Sodium-Hydrogen Exchanger (NHE) - Empagliflozin reduces intracellular pH and calcium signaling by inhibiting NHE. This decreases fibroblast activity and collagen production, which are key contributors to fibrosis[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://cardiab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12933-023-01756-0?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "1").
2. Reduction of Oxidative Stress - It lowers oxidative stress by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which helps prevent tissue damage and fibrosis[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/18/3/313?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "2").
3. Modulation of Fibrotic Pathways - Empagliflozin inhibits the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway, a major driver of fibrosis, thereby reducing extracellular matrix deposition[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://cardiab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12933-021-01322-6?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "3
Recent Clinical Trials on Empagliflozin
1. **EMPACT-MI Phase III Trial**: This trial investigated the effect of empagliflozin (Jardiance) on the risk of heart failure hospitalization and death in adults following a heart attack. The trial showed a 10% relative risk reduction in the primary composite endpoint of time to first hospitalization due to heart failure or all-cause mortality for empagliflozin versus placebo(https://www.boehringer-ingelheim.com/human-health/heart-diseases/results-jardiance-empact-mi-phase-iii-trial?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "1").
2. **Comparative Outcomes of Empagliflozin to Dapagliflozin in Patients With Heart Failure**: This cohort study compared the outcomes of empagliflozin and dapagliflozin in reducing all-cause mortality and hospitalizations in patients with heart failure. The study found that patients who started using empagliflozin were less likely to experience the primary outcome of composite of all-cause mortality or hospitalization compared with those who started using dapagliflozin[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2818219?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "2").
3. **EMPEROR-Reduced Trial**: This trial assessed the safety and efficacy of empagliflozin in patients with symptomatic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), irrespective of diabetes status. The trial showed that empagliflozin is superior to placebo in improving heart failure outcomes among patients with HFrEF[43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054](https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/clinical-trials/2020/08/28/16/12/emperor-reduced?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "3").
If you have any specific questions or need more detailed information or full text article feel free to ask or send a mail arunthakur@p4medicine.in
Above is a medical information only not for use please consult your doctor for any query.
EMPAM L is a combination of Empagliflozin 10 MG and Linagliptin 5 MG, a medication used to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
This rational combination helps provide organ protection and life-saving benefits, reducing the risk of kidney damage, nerve problems, and cardiovascular complications.
Recent Clinical Trials on DPP-4 Inhibitors:
Prescribing Information:
EMPAM L is a combination of Empagliflozin 10 MG and Linagliptin 5 MG, a medication used to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is not recommended for patients with type 1 diabetes or in diabetic ketoacidosis.
Dosage & Administration:
Starting dose: Empagliflozin 10 MG / Linagliptin 5 MG once daily.
If additional glycemic control is needed, increase to Empagliflozin 25 MG / Linagliptin 5 MG once daily. Can be taken with or without food. Warnings & Precautions: Pancreatitis: Cases of acute pancreatitis, including fatal ones, discontinue if suspected.
Heart Failure: Some DPP-4 inhibitors have been linked to heart failure. Monitor patients at risk.
Renal Impairment: Not recommended for patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease.
Necrotizing Fasciitis (Fournier’s Gangrene): If symptoms appear, immediate medical intervention is required. (https://pro.boehringer-ingelheim.com/in/products/glyxambi/prescribing-information?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "1").
This rational combination helps provide organ protection and life-saving benefits, reducing the risk of kidney damage, nerve problems, and cardiovascular complications.
- 1. Improve Glycemic Control: Lowers HbA1c levels.
- 2. Weight Loss: Promotes weight loss due to increased glucose excretion.
- 3. Blood Pressure Reduction: Helps lower blood pressure.
- 4. Complementary Mechanisms: Combining SGLT2 inhibition with DPP-4 inhibition.
- 5. Low Risk of Hypoglycemia: Suitable for patients at risk of hypoglycemia.
- 6. No Weight Gain: Neutral effect on weight.
Recent Clinical Trials on DPP-4 Inhibitors:
- Comprehensive Review of DPP-4 Inhibitors:This review examines the potential of DPP-4 inhibitors in managing type 2 diabetes. It highlights their safety, tolerability, and low risk of hypoglycemia, making them an attractive treatment option. The review also explores their long-term safety and potential influence on immune function and susceptibility to COVID-19.
- Systematic Review of Structure-Activity Relationship Studies: This review summarizes recent advances related to DPP-4 inhibitors, focusing on their biochemical characteristics and pharmacological principles.
- Practical Approach for Type 2 Diabetes: Role of DPP-4 Inhibitors: This article discusses the role of DPP-4 inhibitors in managing type 2 diabetes, highlighting their efficacy in controlling blood sugar levels.
Prescribing Information:
EMPAM L is a combination of Empagliflozin 10 MG and Linagliptin 5 MG, a medication used to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is not recommended for patients with type 1 diabetes or in diabetic ketoacidosis.
Dosage & Administration:
Starting dose: Empagliflozin 10 MG / Linagliptin 5 MG once daily.
If additional glycemic control is needed, increase to Empagliflozin 25 MG / Linagliptin 5 MG once daily. Can be taken with or without food. Warnings & Precautions: Pancreatitis: Cases of acute pancreatitis, including fatal ones, discontinue if suspected.
Heart Failure: Some DPP-4 inhibitors have been linked to heart failure. Monitor patients at risk.
Renal Impairment: Not recommended for patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease.
Necrotizing Fasciitis (Fournier’s Gangrene): If symptoms appear, immediate medical intervention is required. (https://pro.boehringer-ingelheim.com/in/products/glyxambi/prescribing-information?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054 "1").

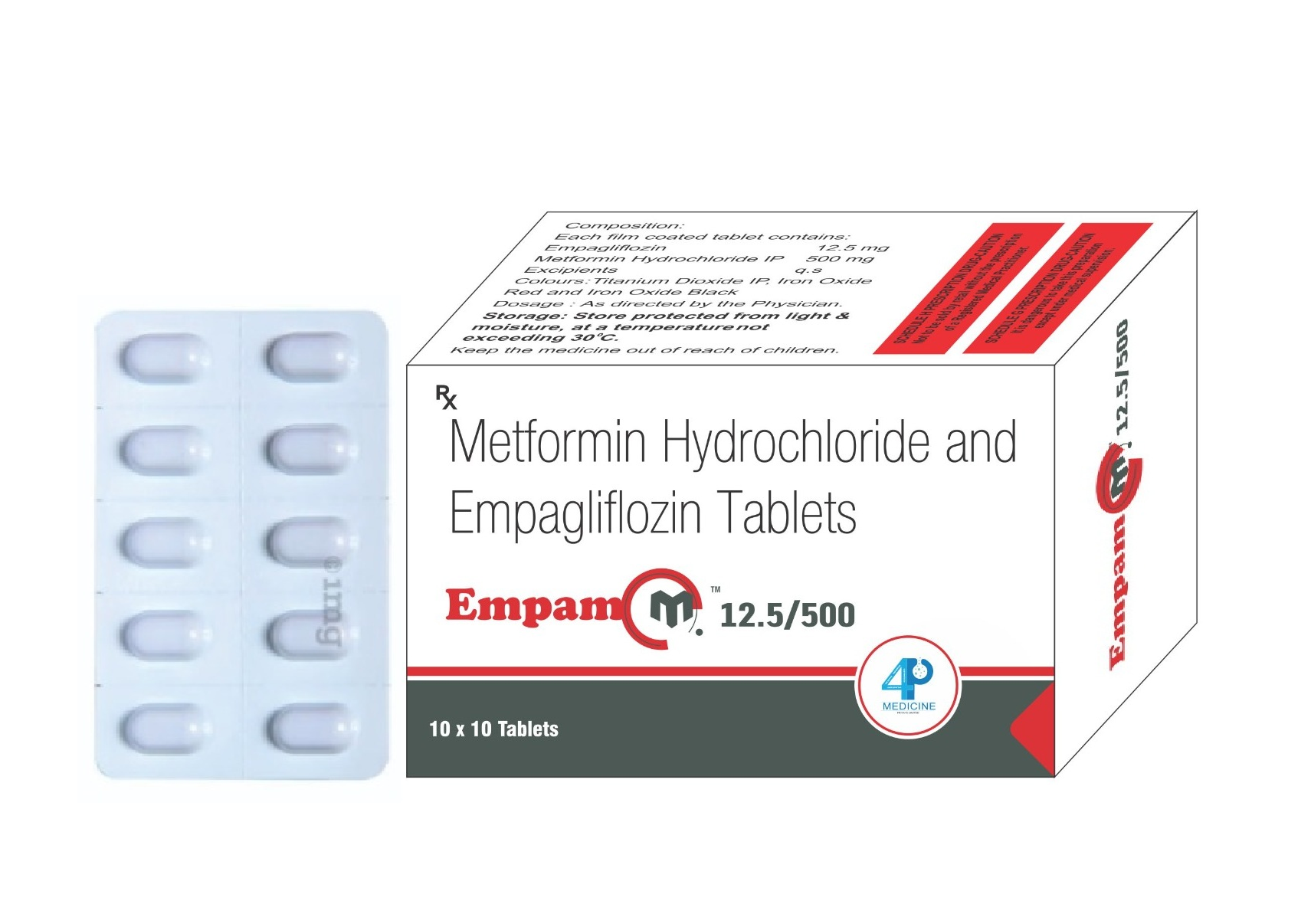
EMPAM M Empagliflozin and Metformin Combination with two strength
EMPAM M Empagliflazon 12.5 MG and Metformin 500 MG EMPAM M Empagliflazon 12.5 MG and Metformin 1000 MG
This is a combination of Empagliflozin SGLT2 inhibitor and metformin a biguanide have a complementary action and a synergistic effect to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), addressing multiple pathophysiological pathways.
Dual Mechanism of Action
Empagliflozin a SGLT2 receptors inhibitors inhibit glucose absorption in Kidney and promote urinary glucose excretion. Metformin Suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis and enhances peripheral insulin sensitivity.
Glycemic Control Targets both fasting (metformin) and postprandial (Empagliflozin) hyperglycemia. Cardiovascular Benefits
Empagliflozin reduces cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization for heart failure. Weight loss Effects
Empagliflozin promotes weight loss (~2–3 kg) via caloric excretion; metformin is weight-neutral or modestly reduces weight. Low Hypoglycemia Risk
Both agents have minimal hypoglycemia risk when used alone or in combination EMPAM M Benefits 1. Enhanced Glycemic Control Greater HbA1c reduction compared to either monotherapy, particularly in patients with inadequate control on metformin alone.
2. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Empagliflozin demonstrated a 38% reduction in cardiovascular death in high-risk patients (EMPA-REG OUTCOME).
3. Weight Loss Combined therapy leads to clinically meaningful weight reduction, beneficial for overweight/obese patients.
4. Renal Protection Empagliflozin reduces risk of worsening nephropathy by 39% (EMPA-REG OUTCOME).
5. Hypoglycemia Safety Suitable for patients at risk of hypoglycemia (e.g., elderly, renal impairment).
6. Convenience - Fixed-dose combinations simplify regimens and improve adherence.
References 1. **EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial**: - Zinman B, et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. *N Engl J Med.* 2015;373:2117–28. - Demonstrated CV and renal benefits of empagliflozin.
2. **Metformin Efficacy**: UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes. *Lancet.* 1998;352(9131):854–65.
3. **ADA/EASD Guidelines**: - Davies MJ, et al. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2022. *Diabetes Care.* 2022;45(12):2753–86. - Recommends SGLT2 inhibitors (e.g., empagliflozin) for patients with CVD/HF/CKD.
4. **Combination Therapy Review**: - Abdul-Ghani M, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors and metformin: Dual antihyperglycemic therapy for type 2 diabetes. *Diabetes Ther.* 2018;9(3):953–63.
Clinical Considerations
Contraindications Avoid in severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m² for empagliflozin; <30 for metformin).
Side Effects
Empagliflozin may increase UTI/genital mycotic infections; metformin can cause GI disturbances.
This combination is particularly advantageous for T2DM patients with CVD, heart failure, obesity, or early-stage CKD, aligning with modern precision medicine approaches.
This is not for medical use this is for a information for use consult your physician.
Empagliflozin a SGLT2 receptors inhibitors inhibit glucose absorption in Kidney and promote urinary glucose excretion. Metformin Suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis and enhances peripheral insulin sensitivity.
Glycemic Control Targets both fasting (metformin) and postprandial (Empagliflozin) hyperglycemia. Cardiovascular Benefits
Empagliflozin reduces cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization for heart failure. Weight loss Effects
Empagliflozin promotes weight loss (~2–3 kg) via caloric excretion; metformin is weight-neutral or modestly reduces weight. Low Hypoglycemia Risk
Both agents have minimal hypoglycemia risk when used alone or in combination EMPAM M Benefits 1. Enhanced Glycemic Control Greater HbA1c reduction compared to either monotherapy, particularly in patients with inadequate control on metformin alone.
2. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Empagliflozin demonstrated a 38% reduction in cardiovascular death in high-risk patients (EMPA-REG OUTCOME).
3. Weight Loss Combined therapy leads to clinically meaningful weight reduction, beneficial for overweight/obese patients.
4. Renal Protection Empagliflozin reduces risk of worsening nephropathy by 39% (EMPA-REG OUTCOME).
5. Hypoglycemia Safety Suitable for patients at risk of hypoglycemia (e.g., elderly, renal impairment).
6. Convenience - Fixed-dose combinations simplify regimens and improve adherence.
References 1. **EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial**: - Zinman B, et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. *N Engl J Med.* 2015;373:2117–28. - Demonstrated CV and renal benefits of empagliflozin.
2. **Metformin Efficacy**: UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes. *Lancet.* 1998;352(9131):854–65.
3. **ADA/EASD Guidelines**: - Davies MJ, et al. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2022. *Diabetes Care.* 2022;45(12):2753–86. - Recommends SGLT2 inhibitors (e.g., empagliflozin) for patients with CVD/HF/CKD.
4. **Combination Therapy Review**: - Abdul-Ghani M, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors and metformin: Dual antihyperglycemic therapy for type 2 diabetes. *Diabetes Ther.* 2018;9(3):953–63.
Clinical Considerations
Contraindications Avoid in severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m² for empagliflozin; <30 for metformin).
Side Effects
Empagliflozin may increase UTI/genital mycotic infections; metformin can cause GI disturbances.
This combination is particularly advantageous for T2DM patients with CVD, heart failure, obesity, or early-stage CKD, aligning with modern precision medicine approaches.
This is not for medical use this is for a information for use consult your physician.
tandc
